Abstract
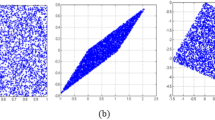
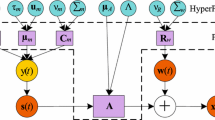
The task of recovering a set of unknown sources from another set of mixtures directly observable and little more information about the way they were mixed is called the blind source separation problem. If the assumption in order to obtain the original sources is their statistical independence, then ICA (Independent Component Analysis) may be the technique to recover the signals. In this contribution, we propose and analyze three evaluation functions (contrast functions in Independent Component Analysis terminology) for the use in a genetic algorithm (PNL-GABSS, Post-NonLinear Genetic Algorithm for Blind Source Separation) which solves source separation in nonlinear mixtures, assuming the post-nonlinear mixture model. A thorough analysis of the performance of the chosen contrast functions is made by means of ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), showing the validity of the three approaches.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hyvärinen, A., Karhunen, J., Oja, E.: Independent Component Analysis. John Wiley, New York (2001)
Burel, G.: Blind separation of sources: a nonlinear neural algorithm. Neural Networks 5, 937–947 (1992)
Lee, T.W., Koehler, B., Orglmeister, R.: Blind source separation of nonlinear mixing models. In: Neural Networks for Signal Processing VII, pp. 406–415. IEEE Press, Los Alamitos (1997)
Hyvärinen, A., Pajunen, P.: Nonlinear independent component analysis: Existence and uniqueness results. Neural Networks 12, 429–439 (1999)
Taleb, A., Jutten, C.: Source separation in post-nonlinear mixtures. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 47, 2807–2820 (1999)
Rojas, I., Puntonet, C., Cañas, A., Pino, B., Fernández, J., Rojas, F.: Genetic algorithms for the blind separation of sources. In: IASTED (2001)
Rojas, F., Puntonet, C., Rodríguez, M., Rojas, I., Clemente, R.: Blind source separation in post-nonlinear mixtures using competitive learning, simulated annealing and a genetic algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part C 34, 407–416 (2004)
Cardoso, J.F., Souloumiac, A.: Blind beamforming for non Gaussian signals. IEE Proceedings-F 140, 362–370 (1993)
Michalewicz, Z.: Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs, Tercera edn. Springer, New York (1999)
Amari, S.I., Cichocki, A., Yang, H.: A new learning algorithm for blind source separation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 8, pp. 757–763. MIT Press, Cambridge (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rojas, F., Górriz, J.M., Valenzuela, O. (2005). Analysis of Variance of Three Contrast Functions in a Genetic Algorithm for Non-linear Blind Source Separation. In: Cabestany, J., Prieto, A., Sandoval, F. (eds) Computational Intelligence and Bioinspired Systems. IWANN 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3512. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11494669_128
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11494669_128
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26208-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32106-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)