Abstract
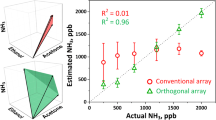
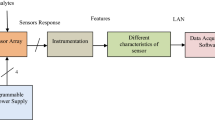
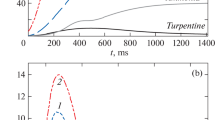
Traditional approaches to gas sensing are usually related with gas identification and classification, i.e., recognition of aromas. In this work we propose an innovative approach to determine the concentration of the single species in a gas mixture by using nonlinear source separation techniques. Additionally, responses of tin oxide sensor arrays were analyzed using nonlinear regression techniques to determine the concentrations of ammonia and acetone in gas mixtures. The use of the source separation approach allows the compensation of some of the most important sensor disadvantages: the parameter spreading and time drift.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herault, J., Jutten, C.: Blind separation of sources, Part I: An adaptive algorithm based on neuromimetic structure. Signal Processing 24, 1–10 (1991)
Moss, S.D., Johnson, C.C., Janata, J.: Hydrogen, Calcium and Potassium Ion-Sensitive FET Transducers: A preliminary Report. IEEE Trans. on Biomedical engineering 25(1), 49–56 (1978)
Taleb, A., Jutten, C.: Source Separation in Post-Non linear Mixtures. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 47(10), 2807–2820 (1999)
Comon, P.: Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Processing 36, 287–314 (1994)
Solazzi, M., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Blind source separation in nonlinear mixtures by adaptive spline neural networks. In: Proc. Int. Conf. on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation (ICA 2001), San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 254–259 (2001)
Ziehe, A., Kawanabe, M., Harmeling, S., Muller, K.-R.: Separation of post-nonlinear mixtures using ACE and temporal decorrelation. In: Proc. Int. Conf. on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation (ICA 2001), San Diego, USA, pp. 433–438 (2001)
Ziehe, A., Kawanabe, M., Harmeling, S., Muller, K.-R.: Blind separation of post-nonlinear mixtures using gaussianizing transformations and temporal decorrelation, Nara, Japan (2003)
Harmeling, S., Ziehe, A., Kawanabe, M., Muller, K.-R.: Kernel feature spaces and nonlinear blind source separation. In: Dietterich, T.G., Becker, S., Ghahramani, Z. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 14, pp. 761–768. MIT Press, Cambridge (2002)
Scholkopf, B.: Statistical Learning And Kernel methods. Technical report MSR-TR-2000-23. Microsoft research. Gunne, Germany (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bedoya, G., Bermejo, S., Cabestany, J. (2005). Multichannel Blind Signal Separation in Semiconductor-Based GAS Sensor Arrays. In: Cabestany, J., Prieto, A., Sandoval, F. (eds) Computational Intelligence and Bioinspired Systems. IWANN 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3512. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11494669_130
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11494669_130
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26208-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32106-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)