Abstract
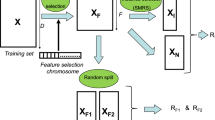
We propose a local feature selection method for the Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) framework. Unlike conventional feature selection algorithms that assign a global set of features to the whole data set, our algorithm, called Multiple Instance Local Salient Feature Selection (MI-LSFS), searches the feature space to find the relevant features within each bag. We also propose a new multiple instance classification algorithm, called Multiple Instance Learning via Embedded Structures with Local Feature Selection (MILES-LFS), by integrating the information learned by MI-LSFS during the feature selection process. In MILES-LFS, we use information learned by MI-LSFS to identify a reduced subset of representative bags. For each representative bag, we identify its most representative instances. Using the instance prototypes of all representative bags and their relevant features, we project and map the MIL data to a standard feature vector data. Finally, we train a 1-Norm support vector machine (1-Norm SVM) to learn the classifier. We investigate the performance of MI-LSFS in selecting the local relevant features using synthetic and benchmark data sets. The results confirm that MI-LSFS can identify the relevant features for each bag. We also investigate the performance of the proposed MILES-LFS algorithm on several synthetic and real benchmark data sets. The results confirm that MILES-LFS has a robust classification performance comparable to the well-known MILES algorithm. More importantly, our results confirm that using the reduced set of prototypes to project the MIL data reduces the computational time significantly without affecting the classification accuracy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Amores, J. (2013). Multiple instance classification: review, taxonomy and comparative study. Artificial Intelligence, 201, 81–105.
Andrews, S., Tsochantaridis, I., & Hofmann, T. (2003). Support vector machines for multiple-instance learning. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 577–584).
Ang, J.C, Mirzal, A., Haron, H., & Hamed, H.N.A. (2015). Supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised feature selection: a review on gene selection. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 13(5), 971–989.
Arai, H., Maung, C., Xu, K., & Schweitzer, H. (2016). Unsupervised feature selection by heuristic search with provable bounds on suboptimality. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 666–672).
Archibald, R., & Fann, G. (2007). Feature selection and classification of hyperspectral images with support vector machines. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 4(4), 674–677.
Armanfard, N., Reilly, J.P., & Komeili, M. (2015). Local feature selection for data classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 38(6), 1217–1227.
Armanfard, N., Reilly, J.P., & Komeili, M. (2018). Logistic localized modeling of the sample space for feature selection and classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(5), 1396–1413.
Battiti, R. (1994). Using mutual information for selecting features in supervised neural net learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5(4), 537–550.
Bolón-Canedo, V., Sánchez-Maroño, N., & Alonso-Betanzos, A. (2013). A review of feature selection methods on synthetic data. Knowledge and Information Systems, 34(3), 483–519.
Boyd, S., & Vandenberghe, L. (2004). Convex optimization. Cambridge University press.
Chai, J., Chen, H., Huang, L., & Shang, F. (2014). Maximum margin multiple-instance feature weighting. Pattern Recognition, 47(6), 2091–2103.
Chai, J., Chen, Z., Chen, H., & Ding, X. (2016). Designing bag-level multiple-instance feature-weighting algorithms based on the large margin principle. Information Sciences, 367, 783–808.
Chen, B., Liu, H., Chai, J., & Bao, Z. (2008). Large margin feature weighting method via linear programming. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(10), 1475–1488.
Chen, Y., Bi, J., & Wang, J.Z. (2006). Miles: Multiple-instance learning via embedded instance selection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(12), 1931–1947.
Dietterich, T. G., Lathrop, R.H., & Lozano-Pérez, T. (1997). Solving the multiple instance problem with axis-parallel rectangles. Artificial Intelligence, 89 (1-2), 31–71.
Faris, H., Hassonah, M.A., Ala’m, A.Z., Mirjalili, S., & Aljarah, I. (2018). A multi-verse optimizer approach for feature selection and optimizing svm parameters based on a robust system architecture. Neural Computing and Applications, 30 (8), 2355–2369.
Fleuret, F. (2004). Fast binary feature selection with conditional mutual information. Journal of Machine learning research, 5, 1531–1555.
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2001). The elements of statistical learning Vol. 1. New York: Springer Series in Statistics.
Guyon, I., & Elisseeff, A. (2003). An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3(Mar), 1157–1182.
Guyon, I., Gunn, S., Nikravesh, M., & Zadeh, L.A. (2008). Feature extraction: foundations and applications Vol. 207. Berlin: Springer.
Guyon, I., Weston, J., Barnhill, S., & Vapnik, V. (2002). Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine Learning, 46(1-3), 389–422.
Hubert, L., & Arabie, P. (1985). Comparing partitions. Journal of Classification, 2(1), 193–218.
Jolliffe, I. T. (1986). Principal components in regression analysis. In Principal component analysis (pp. 129–155). Springer.
Karem, A., Trabelsi, M., Moalla, M., & Frigui, H. (2018). Comparison of several single and multiple instance learning methods for detecting buried explosive objects using gpr data. In Detection and sensing of mines, explosive objects, and obscured targets XXIII, (Vol. 10628 p. 106280G). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Kim, S., & Choi, S. (2010). Local dimensionality reduction for multiple instance learning. In 2010 IEEE International workshop on machine learning for signal processing (pp. 13–18). IEEE.
Kira, K., & Rendell, L.A. (1992). A practical approach to feature selection. In Machine Learning Proceedings 1992 (pp. 249–256). Elsevier.
Kohavi, R., John, G. H., & et al. (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence, 97(1-2), 273–324.
Kononenko, I. (1994). Estimating attributes: analysis and extensions of relief. In European conference on machine learning (pp. 171–182). Springer.
Kumar, V., & Minz, S. (2014). Feature selection: a literature review. SmartCR, 4(3), 211–229.
Lango, M., & Stefanowski, J. (2018). Multi-class and feature selection extensions of roughly balanced bagging for imbalanced data. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 50(1), 97–127.
Lazar, C., Taminau, J., Meganck, S., Steenhoff, D., Coletta, A., Molter, C., de Schaetzen, V., Duque, R., Bersini, H., & Nowe, A. (2012). A survey on filter techniques for feature selection in gene expression microarray analysis. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (TCBB), 9(4), 1106–1119.
LeCun, Y., Cortes, C., & Burges, C.J. (1998). The mnist database of handwritten digits. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist10(34), 14.
Li, J., Cheng, K., Wang, S., Morstatter, F., Trevino, R.P., Tang, J., & Liu, H. (2017a). Feature selection: a data perspective. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 50(6), 1–45.
Li, Y., Li, T., & Liu, H. (2017b). Recent advances in feature selection and its applications. Knowledge and Information Systems, 53(3), 551–577.
Lim, H., & Kim, D. W. (2020). Mfc: Initialization method for multi-label feature selection based on conditional mutual information. Neurocomputing, 382, 40–51.
Maron, O., & Lozano-Pérez, T. (1998). A framework for multiple-instance learning. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 570–576).
Matthews, B.W. (1975). Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of t4 phage lysozyme. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure, 405(2), 442–451.
Neumann, J., Schnörr, C., & Steidl, G. (2005). Combined svm-based feature selection and classification. Machine Learning, 61(1-3), 129–150.
Qi, X., & Han, Y. (2007). Incorporating multiple svms for automatic image annotation. Pattern Recognition, 40(2), 728–741.
Rand, W.M. (1971). Objective criteria for the evaluation of clustering methods. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 66(336), 846–850.
Raykar, V.C., Krishnapuram, B., Bi, J., Dundar, M., & Rao, R.B. (2008). Bayesian multiple instance learning: automatic feature selection and inductive transfer. In Proceedings of the 25th international conference on machine learning (pp. 808–815).
Saeys, Y., Abeel, T., & Van de Peer, Y. (2008). Robust feature selection using ensemble feature selection techniques. In Joint european conference on machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases (pp. 313–325). Springer.
Saeys, Y., Inza, I., & Larrañaga, P. (2007). A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 23(19), 2507–2517.
Safta, W., Farhangi, M.M., Veasey, B., Amini, A., & Frigui, H. (2019). Multiple instance learning for malignant vs. benign classification of lung nodules in thoracic screening ct data. In 2019 IEEE 16Th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2019) (pp. 1220–1224).
Sayed, S., Nassef, M., Badr, A., & Farag, I. (2019). A nested genetic algorithm for feature selection in high-dimensional cancer microarray datasets. Expert Systems with Applications, 121, 233–243.
Shishkin, A., Bezzubtseva, A., Drutsa, A., Shishkov, I., Gladkikh, E., Gusev, G., & Serdyukov, P. (2016). Efficient high-order interaction-aware feature selection based on conditional mutual information. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 4637–4645).
Sun, Y. (2007). Iterative relief for feature weighting: algorithms, theories, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(6), 1035–1051.
Sun, Y. Y., Ng, M. K., & Zhou, Z. H. (2010). Multi-instance dimensionality reduction. In AAAI. Citeseer.
Tafazzoli, F., & Frigui, H. (2016). Vehicle make and model recognition using local features and logo detection. In 2016 International symposium on signal, image, video and communications (ISIVC) (pp. 353–358). IEEE.
Tai, L. K., Setyonugroho, W., & Chen, A. L. (2020). Finding discriminatory features from electronic health records for depression prediction. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 55(2), 371–396.
Tan, F., Fu, X., Zhang, Y., & Bourgeois, A. G. (2008). A genetic algorithm-based method for feature subset selection. Soft Computing, 12(2), 111–120.
Torkkola, K. (2003). Feature extraction by non-parametric mutual information maximization. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3(Mar), 1415–1438.
Uġuz, H. (2011). A two-stage feature selection method for text categorization by using information gain, principal component analysis and genetic algorithm. Knowledge-Based Systems, 24(7), 1024–1032.
Urbanowicz, R. J., Meeker, M., La Cava, W., Olson, R. S., & Moore, J. H. (2018). Relief-based feature selection: Introduction and review. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 85, 189–203.
Wang, J., & Zucker J.D. (2000). Solving multiple-instance problem: A lazy learning approach.
Weinberger, K. Q., & Saul, L. K. (2009). Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(2).
Yang, Y., Shen, H. T., Ma, Z., Huang, Z., & Zhou, X. (2011). L 2, 1-norm regularized discriminative feature selection for unsupervised learning. In IJCAI International joint conference on artificial intelligence.
Yuan, X., Hua, X. S., Wang, M., Qi, G. J., & Wu, X. Q. (2007). A novel multiple instance learning approach for image retrieval based on adaboost feature selection. In 2007 IEEE International conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 1491–1494). IEEE.
Zafra, A., Pechenizkiy, M., & Ventura, S. (2012). Relieff-mi: an extension of relieff to multiple instance learning. Neurocomputing, 75(1), 210–218.
Zafra, A., Pechenizkiy, M., & Ventura, S. (2013). Hydr-mi: a hybrid algorithm to reduce dimensionality in multiple instance learning. Information Sciences, 222, 282–301.
Zhang, M. L., & Zhou, Z. H. (2004). Improve multi-instance neural networks through feature selection. Neural Processing Letters, 19(1), 1–10.
Zhou, Z. H., & Zhang, M. L. (2002). Neural networks for multi-instance learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Technology (pp. 455–459). Beijing.
Zhu, H., Liao, L. Z., & Ng, M. K. (2018). Multi-instance dimensionality reduction via sparsity and orthogonality. Neural Computation, 30(12), 3281–3308.
Zhu, J., Rosset, S., Tibshirani, R., & Hastie, T.J. (2004). 1-norm support vector machines. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 49–56).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Availability of data and material
The data sets generated during and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahrjooihaghighi, A., Frigui, H. Local feature selection for multiple instance learning. J Intell Inf Syst 59, 45–69 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-021-00680-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-021-00680-7