Creating a REST API Backend using Node.js, Express and Postgres
Last Updated :
16 Sep, 2024
Creating a REST API backend with Node.js, Express, and PostgreSQL offers a powerful, scalable solution for server-side development. It enables efficient data management and seamless integration with modern web applications.
This backend can do Query operations on the PostgreSQL database and provide the status or data on the REST API.
Installation Requirement:
Node.js:
PostgreSQL:
Testing for Successful Installation
Node.js:
Open Command Prompt or Terminal and type:
node -v
The output must show some version number example:
v12.14.0
Note: If it shows command not found then node.js is not installed successfully.
Postgres:
Windows: Search for SQL Shell, if found the Installation is successful.
Linux or Mac: Type the command below:
which psql
Note: If output present then it is installed successfully.
Steps to Setup Database
Step 1: Open the PostgreSQL Shell
Step 2: Type the Database Credentials for local Setup or press enter in case you want to go with default values as shown below: 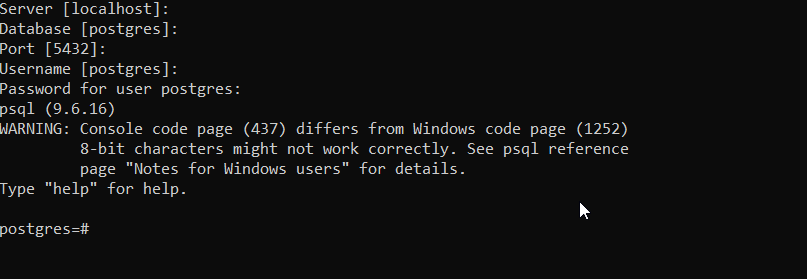
Step 3: Create the database using:
create database gfgbackend;
Step 4: Switch to this database using:
\c gfgbackend;
Step 5: Create a test table using:
create table test(id int not null);
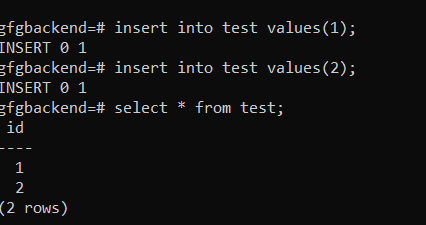
Step 6: Insert values into test table using:
insert into test values(1);
insert into test values(2);
Step 7: Now try to validate whether the data is inserted into table using:
select * from test;
Steps to Create a Backend
Step 1: Go to the Directory where you want to create project
Step 2: Initialize the Node Project using:
npm init
Step 3: Type the name of Project and Other Details or Press Enter if you want to go with Default 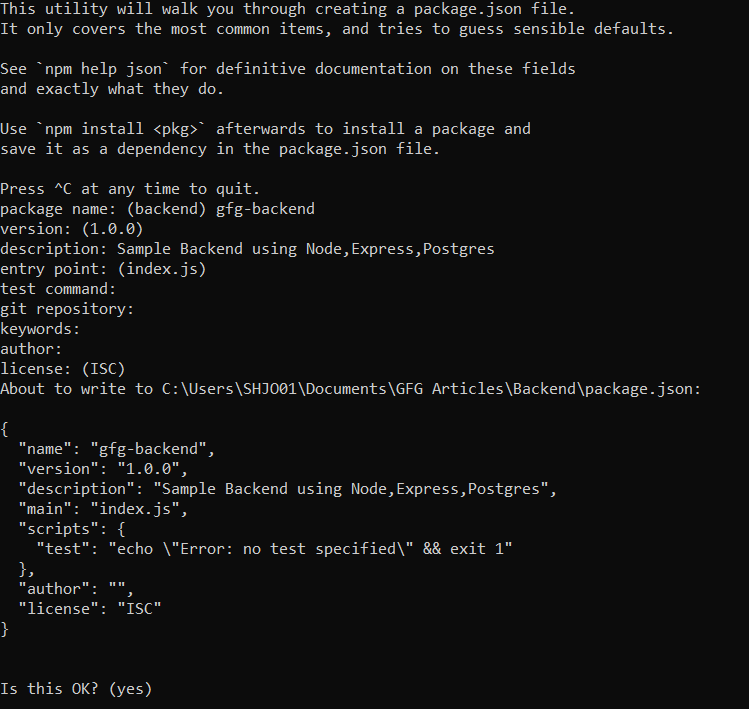
Step 4: Install express using npm
npm install --save express
Step 5: Install the node-postgres Client using npm
npm install --save pg
Step 6: Install the postgres module for serializing and de-serializing JSON data in to hstore format using npm.
npm install --save pg-hstore
Step 7: Create a file index.js as entry point to the backend.
Now, Install body-parser using npm
npm install --save body-parser
Example: Now add the below code to index.js file which initiates the express server, creates a pool connection and also creates a REST API ‘/testdata’. Don’t forget to add your Password while pool creation in the below code.
JavaScript
// Filename - index.js
// Entry Point of the API Server
const express = require('express');
/* Creates an Express application.
The express() function is a top-level
function exported by the express module.
*/
const app = express();
const Pool = require('pg').Pool;
const pool = new Pool({
user: 'postgres',
host: 'localhost',
database: 'gfgbackend',
password: 'postgres',
dialect: 'postgres',
port: 5432
});
/* To handle the HTTP Methods Body Parser
is used, Generally used to extract the
entire body portion of an incoming
request stream and exposes it on req.body
*/
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
pool.connect((err, client, release) => {
if (err) {
return console.error(
'Error acquiring client', err.stack)
}
client.query('SELECT NOW()', (err, result) => {
release()
if (err) {
return console.error(
'Error executing query', err.stack)
}
console.log("Connected to Database !")
})
})
app.get('/testdata', (req, res, next) => {
console.log("TEST DATA :");
pool.query('Select * from test')
.then(testData => {
console.log(testData);
res.send(testData.rows);
})
})
// Require the Routes API
// Create a Server and run it on the port 3000
const server = app.listen(3000, function () {
let host = server.address().address
let port = server.address().port
// Starting the Server at the port 3000
})
Step to Run the Backend: Now, start the backend server using:
node index.js
Open Browser and try to router to:
http://localhost:3000/testdata
Now, you can see the data from test table as follows: 
Conclusion
Creating a REST API backend using Node.js, Express, and PostgreSQL provides a scalable and efficient solution for building modern web applications. This stack offers easy integration, robust data handling, and flexibility, making it ideal for backend development needs.
Similar Reads
Creating a REST API Backend using Node.js, Express and Postgres
Creating a REST API backend with Node.js, Express, and PostgreSQL offers a powerful, scalable solution for server-side development. It enables efficient data management and seamless integration with modern web applications. This backend can do Query operations on the PostgreSQL database and provide
4 min read
Health Tracker App Backend Using Node and Express.js
A Health Tracker App is a platform that allows users to log and monitor various data of their health and fitness. In this article, we are going to develop a Health Tracker App with Node.js and Express.js. that allows users to track their health-related activities such as exercise, meals, water intak
4 min read
Real-Time Auction Platform using Node and Express.js
The project is a Real-Time Auction Platform developed using Node.js Express.js and MongoDB database for storing details where users can browse different categories of products, view ongoing auctions, bid on items, and manage their accounts. The platform also allows sellers to list their products for
12 min read
How to Build a RESTful API Using Node, Express, and MongoDB ?
This article guides developers through the process of creating a RESTful API using Node.js, Express.js, and MongoDB. It covers setting up the environment, defining routes, implementing CRUD operations, and integrating with MongoDB for data storage, providing a comprehensive introduction to building
6 min read
How to create routes using Express and Postman?
In this article we are going to implement different HTTP routes using Express JS and Postman. Server side routes are different endpoints of a application that are used to exchange data from client side to server side. Express.js is a framework that works on top of Node.js server to simplify its APIs
3 min read
RESTful Blogging API with Node and Express.js
Blogs Websites have become very popular nowadays for sharing your thoughts among the users over internet. In this article, you will be guided through creating a Restful API for the Blogging website with the help of Node, Express, and MongoDB. Prerequisites:Node JS & NPMExpress JSMongoDBApproach
6 min read
Node.js Building simple REST API in express
Let's have a brief introduction about the Express framework before starting the code section:Express: It is an open-source NodeJs web application framework designed to develop websites, web applications, and APIs in a pretty easier way. Express helps us to handle different HTTP requests at specific
2 min read
How to create a basic server using Express?
Express is a web application framework for NodeJS, simplifying the process of building robust and scalable web applications. It offers a simple design, making it easy to create APIs and handle HTTP requests and also support the middleware. Express is a popular choice for creating web servers and API
1 min read
Steps to Create an Express.js Application
Creating an Express.js application involves several steps that guide you through setting up a basic server to handle complex routes and middleware. Express.js is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. Here’s a
10 min read
Travel Planning App API using Node & Express.js
In this article, we’ll walk through the step-by-step process of creating a Travel Planning App With Node and ExpressJS. This application will provide users with the ability to plan their trips by searching for destinations, booking flights and hotels, submitting reviews, receiving notifications, sha
10 min read