In this Kubernetes Tutorial you’ll learn all the basics to advanced concepts like Kubernetes service , Kubernetes cluster construction , Kubernetes deployment , Kubernetes Architecture , etc. This free tutorial on Kubernetes will provide all the essential information needed to understand and work with Kubernetes, including the use of APIs, installation, and Kubernetes cluster construction. Whether you are a beginner or an expert, this tutorial will cover all the necessary details to help you learn and understand Kubernetes.
Kubernetes is a tool that helps us to run and manage applications in containers. It was developed by Google Lab in 2014, and it is also known as k8s. It is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, management, and scaling of container-based applications in different kinds of environments like physical, virtual, and cloud-native computing foundations.

Containers are isolated from each other so that multiple containers can run on the same machine without interrupting anyone else. It allows us to deploy and manage container-based applications across a Kubernetes cluster of machines.
Prerequisites for this Kubernetes Tutorial
Before diving into Kubernetes, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of certain concepts and technologies. Here are some prerequisites:
- Have good understanding of Container concept & Container Management Tool like Docker or Podman.
- Understanding of distributed system.
- Understanding of REST API
- Basic understanding of YAML
Basics of Kubernetes
Kubernetes Basics will teach you how to manage these “containers” effectively. Kubernetes is like a ship captain for these containers, organizing and placing them on multiple computers (like a ship carrying many containers). This introduction will explain key Kubernetes ideas like Pods, Services, and Deployments. You’ll learn how Kubernetes keeps your containerized applications running smoothly and efficiently
To dive deeper into how Kubernetes fits within the larger DevOps ecosystem, the DevOps Engineering – Planning to Production course covers Kubernetes from setup to production-level deployment.
Advanced Kubernetes
In this Advanced Kubernetes section we will understand how to manage complex containerized applications. This section assumes you’re familiar with Kubernetes basics and explores powerful features for scaling, security, and automation. We’ll delve into concepts like deployments with rollbacks and health checks, advanced networking configurations for service communication, and tools for managing storage and persistent data for your containerized applications.
Why Do We Need Kubernetes?
There are several reasons to learn Kubernetes like easy scaling of applications, self-healing, portability, and automation. It is very helpful for running microservices and distributed systems.
For example : You have a couple of applications to deploy so, you can package it into a container and run it on a server containing a Docker engine or any other container engine. You package the application into a container using a Docker file and host it on a port for the external world to access it.
But there is a drawback is that it is only running on a single server so, if at that point any failure occurs it becomes an application failure, to handle the single point of failure google introduced Kubernetes to scale applications.
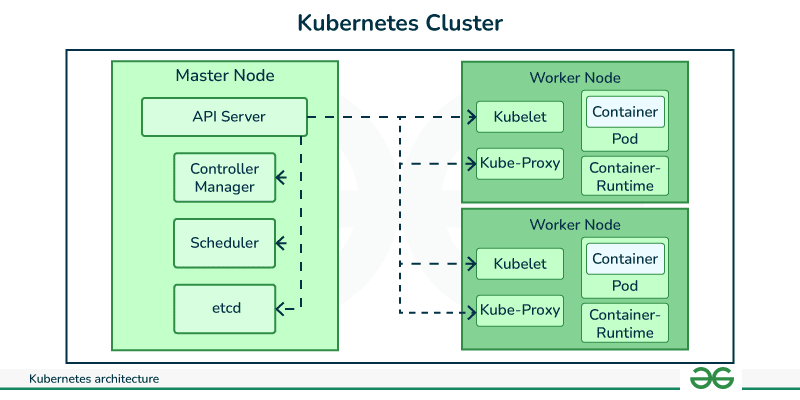
Kubernetes Architecture
Below you will find the image that describe the architecture of Kubernetes.
Features of Kubernetes
- Consistent Development, management, and deployment
- Container-based infrastructure
- Utilization of resources in higher density
- Each component is like a separate unit
- Application-centric infrastructure
- Auto scalability
- Consistency is maintained across testing and development
Advantages of Kubernetes
- Container Orchestration: Kubernetes automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, ensuring efficient resource utilization and seamless deployment updates.
- Scalability: Kubernetes enables horizontal scaling of applications by adding or removing container replicas based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak loads.
- High Availability: With automated health checks and self-healing capabilities, Kubernetes ensures that applications remain available and responsive, reducing downtime and enhancing reliability.
- Fault Tolerance: Kubernetes manages application failures by automatically restarting containers or shifting traffic to healthy instances, improving overall application resilience.
- Flexibility: Supports multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud environments, allowing deployment across various infrastructure providers and on-premises data centers without vendor lock-in.
- Resource Efficiency: Efficiently manages computing resources like CPU and memory, optimizing utilization and reducing costs by scaling resources based on application demands.
- Automated Operations: Simplifies complex operational tasks such as load balancing, storage orchestration, and networking configuration through declarative APIs and automation.
Conclusion
This tutorial provided a comprehensive overview of Kubernetes, including its history, key features, and how it can be used to manage and deliver containerized applications. We covered the use of Kubernetes APIs, installation, and cluster construction. Whether you are new to Kubernetes or an experienced user, this tutorial will provide you with the information you need to understand and work with this powerful open-source platform. Kubernetes is widely used in the industry and continues to be a popular choice for managing containerized applications in a production environment. Keep learning and experimenting with Kubernetes to discover its full potential.
Kubernetes Tutorial – FAQ
How does Kubernetes work?
Kubernetes works by allowing users to define how their applications should run and then automatically handling the deployment, scaling, and management of those applications based on the defined specifications.
What are the key benefits of using Kubernetes?
Some key benefits of using Kubernetes include increased operational efficiency, improved resource utilization, automatic scaling of applications, and enhanced portability across various infrastructure environments.
Is Kubernetes suitable for small businesses?
Yes, Kubernetes can be beneficial for small businesses as it provides a scalable and efficient way to manage containerized applications, enabling them to run seamlessly regardless of the scale.
Are there any alternatives to Kubernetes?
Yes, there are other container orchestration platforms like Docker Swarm and Apache Mesos, but Kubernetes is one of the most popular and widely adopted solutions due to its robust feature set and active community support.
Is Kubernetes a Docker?
Docker is a container runtime, Kubernetes is a platform for running and managing containers from many container runtimes.