The word ‘polymorphism’ means ‘having many forms’. In simple words, we can define Java Polymorphism as the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form. In this article, we will learn what is polymorphism and its type.
Real-life Illustration of Polymorphism in Java: A person can have different characteristics at the same time. Like a man at the same time is a father, a husband, and an employee. So the same person possesses different behaviors in different situations. This is called polymorphism.
What is Polymorphism in Java?
Polymorphism is considered one of the important features of Object-Oriented Programming. Polymorphism allows us to perform a single action in different ways. In other words, polymorphism allows you to define one interface and have multiple implementations. The word “poly” means many and “morphs” means forms, So it means many forms.
Polymorphism enables Java developers to create more flexible and reusable code. Understanding when and how to use it can make your code more maintainable. The Java Programming Course offers practical examples and projects that showcase the power of polymorphism in real-world applications.
Types of Java Polymorphism
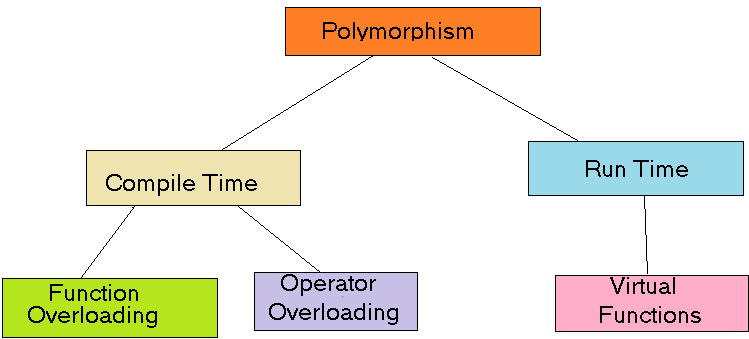
In Java Polymorphism is mainly divided into two types:
- Compile-time Polymorphism
- Runtime Polymorphism
Compile-Time Polymorphism in Java
It is also known as static polymorphism. This type of polymorphism is achieved by function overloading or operator overloading.
Note: But Java doesn’t support the Operator Overloading.
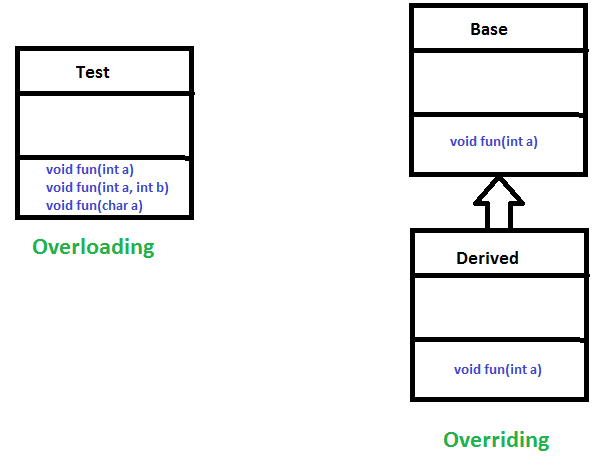
Method Overloading
When there are multiple functions with the same name but different parameters then these functions are said to be overloaded. Functions can be overloaded by changes in the number of arguments or/and a change in the type of arguments.
Example 1:
Java
// Java Program for Method overloading
// By using Different Types of Arguments
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Helper {
// Method with 2 integer parameters
static int Multiply(int a, int b)
{
// Returns product of integer numbers
return a * b;
}
// Method 2
// With same name but with 2 double parameters
static double Multiply(double a, double b)
{
// Returns product of double numbers
return a * b;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Calling method by passing
// input as in arguments
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(2, 4));
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(5.5, 6.3));
}
}
Example 2:
Java
// Java program for Method Overloading
// by Using Different Numbers of Arguments
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Helper {
// Method 1
// Multiplication of 2 numbers
static int Multiply(int a, int b)
{
// Return product
return a * b;
}
// Method 2
// // Multiplication of 3 numbers
static int Multiply(int a, int b, int c)
{
// Return product
return a * b * c;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Calling method by passing
// input as in arguments
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(2, 4));
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(2, 7, 3));
}
}
Subtypes of Compile-time Polymorphism
1. Function Overloading
It is a feature in C++ where multiple functions can have the same name but with different parameter lists. The compiler will decide which function to call based on the number and types of arguments passed to the function.
2. Operator Overloading
It is a feature in C++ where the operators such as +, -, *, etc. can be given additional meanings when applied to user-defined data types.
3. Template
it is a powerful feature in C++ that allows us to write generic functions and classes. A template is a blueprint for creating a family of functions or classes.
It is also known as Dynamic Method Dispatch. It is a process in which a function call to the overridden method is resolved at Runtime. This type of polymorphism is achieved by Method Overriding. Method overriding, on the other hand, occurs when a derived class has a definition for one of the member functions of the base class. That base function is said to be overridden.
Example
Java
// Java Program for Method Overriding
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Parent {
// Method of parent class
void Print()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("parent class");
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
class subclass1 extends Parent {
// Method
void Print() { System.out.println("subclass1"); }
}
// Class 3
// Helper class
class subclass2 extends Parent {
// Method
void Print()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("subclass2");
}
}
// Class 4
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of class 1
Parent a;
// Now we will be calling print methods
// inside main() method
a = new subclass1();
a.Print();
a = new subclass2();
a.Print();
}
}
Outputsubclass1
subclass2
Explanation of the above code:
Here in this program, When an object of a child class is created, then the method inside the child class is called. This is because The method in the parent class is overridden by the child class. Since The method is overridden, This method has more priority than the parent method inside the child class. So, the body inside the child class is executed.
Subtype of Run-time Polymorphism
i. Virtual functions
It allows an object of a derived class to behave as if it were an object of the base class. The derived class can override the virtual function of the base class to provide its own implementation. The function call is resolved at runtime, depending on the actual type of the object.
Diagram –
Polymorphism in Java is a concept that allows objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common class. It enables objects to behave differently based on their specific class type.
Advantages of Polymorphism in Java
- Increases code reusability by allowing objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common class.
- Improves readability and maintainability of code by reducing the amount of code that needs to be written and maintained.
- Supports dynamic binding, enabling the correct method to be called at runtime, based on the actual class of the object.
- Enables objects to be treated as a single type, making it easier to write generic code that can handle objects of different types.
Disadvantages of Polymorphism in Java
- Can make it more difficult to understand the behavior of an object, especially if the code is complex.
- This may lead to performance issues, as polymorphic behavior may require additional computations at runtime.