How to Call an API Continuously from Server Side Itself in Node.js/Express.js ?
Last Updated :
10 Jul, 2024
To call an API continuously from the server side in a Node.js/Express.js environment, you can implement a periodic task that executes at regular intervals. This is typically done using functions such as setInterval, which is built into Node.js for scheduling repeated operations.
There are multiple ways to make API calls from a Node.js server, depending on the level of abstraction you prefer. The easiest method is to use the Axios library.
Set Up a Continuous API Call
You can use setInterval to call the API at regular intervals. The following example will request data from an API every 10 seconds.
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const axios = require('axios');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('API caller is running');
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
// Function to call the API
const callApiContinuously = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/data');
console.log('API Response:', response.data);
// You can handle the response here (e.g., save to database)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error calling API:', error);
}
};
// Call the API every 10 seconds
setInterval(callApiContinuously, 10000);
Note: Replace 'https://api.example.com/data' with the actual API endpoint you want to call.
Steps to Setup Project to call an API
Step 1: Make a folder structure for the project.
mkdir myapp
Step 2: Navigate to the project directory
cd myapp
Step 3: Initialize the NodeJs project inside the myapp folder.
npm init -y
Step 3: Install the necessary packages/libraries in your project using the following commands.
npm install express axios
Project Structure:
The updated dependencies in package.json file will look like:
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.19.2",
"axios": "^1.7.2",
}Example: Implementation to show to call an API continuously from server side.
Node
// app.js
const express = require('express')
const axios = require('axios')
const app = express()
// Post ID tracker
let num = 0
setInterval(() => {
// Increment post tracker
num++
console.log('Wait for 2 second...')
// Make GET Request on every 2 second
axios.get(
`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${num}`)
// Print data
.then(response => {
const { id, title } = response.data
console.log(`Post ${id}: ${title}\n`)
})
// Print error message if occur
.catch(error => console.log(
'Error to fetch data\n'))
}, 2000)
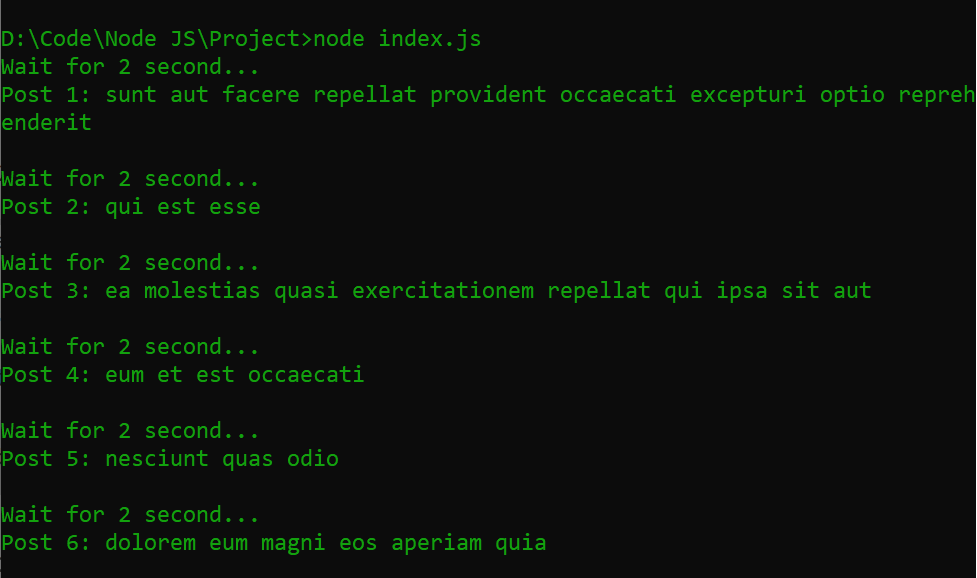
Explanation: In the above example, NodeJS call an API in 2-second intervals to fetch data. If the promise is resolved, then the block will be executed and print data. If a promise rejects, catch block will be executed and print an Error message.
Step to Run Application: Run the application using the following command from the root directory of the project
node app.js
Output:
Example: Implementation to show to call an API continuously from server side doing with POST request.
Node
// app.js
const express = require('express')
const axios = require('axios')
const app = express()
// Dummy database
const posts = [
{
title: 'Headline 1',
id: 1,
body: `sint suscipit perspiciatis velit dolorum
rerum ipsa laboriosam odio`,
userId: 1
},
{
title: 'Headline 2',
id: 2,
body: "fugit voluptas sed molestias voluptatem provident",
userId: 1
},
{
title: 'Headline 3',
id: 3,
body: "voluptate et itaque vero tempora molestiae",
userId: 1
}
]
// Loop over the posts
posts.forEach(post => {
// Post data to API endpoint
axios.post('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/', {
body: post,
})
// Print response
.then(response => {
const { id, title } = response.data.body
console.log(`Post ${id}: ${title}`)
})
// Print error message if occur
.catch(error => console.log(error))
})
Explanation: In the above example, we have created dummy user data. NodeJS makes a POST request to send these data to the API endpoint and print either the response’s data or the error message.
Step to Run Application: Run the application using the following command from the root directory of the project
node app.js
Output:

Similar Reads
How to Call an API Continuously from Server Side Itself in Node.js/Express.js ?
To call an API continuously from the server side in a Node.js/Express.js environment, you can implement a periodic task that executes at regular intervals. This is typically done using functions such as setInterval, which is built into Node.js for scheduling repeated operations. There are multiple w
3 min read
How to Implement Search and Filtering in a REST API with Node.js and Express.js ?
Search and filtering are very basic features that an API must possess to serve data to the client application efficiently. By handling these operations on the server-side, we can reduce the amount of processing that has to be done on the client application, thereby increasing its performance. In thi
5 min read
How to Create a Simple Server in Node.js that Display Hello World ?
We will create a simple server in Node.js that returns Hello World using an express server. Node.js is a powerful JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 engine, commonly used to build scalable network applications. One of the fundamental tasks when learning Node.js is creating a simple server that
2 min read
How to Structure my Application in Express.js ?
Express is a minimalistic framework that is used to create web servers. It is built upon the HTTP module of node.js and provides a much easier way to manage the code related to the server. In this article, we are going to discuss how we can structure our express application. Create Node Project: Ste
4 min read
Health Tracker App Backend Using Node and Express.js
A Health Tracker App is a platform that allows users to log and monitor various data of their health and fitness. In this article, we are going to develop a Health Tracker App with Node.js and Express.js. that allows users to track their health-related activities such as exercise, meals, water intak
4 min read
How to Dynamically Call Router Function in Node.js ?
In Node.js Dynamically calling a router function means that the function is selected at runtime based on the request parameters, instead of being explicitly defined in the code. This can be useful when you want to handle a large number of similar requests without having to define a separate function
4 min read
Node.js Building simple REST API in express
Let's have a brief introduction about the Express framework before starting the code section:Express: It is an open-source NodeJs web application framework designed to develop websites, web applications, and APIs in a pretty easier way. Express helps us to handle different HTTP requests at specific
2 min read
How to create a simple server using Express JS?
In web application development, Express.js is one of the simplified frameworks for the creation of scalable web servers with proper features for building web and mobile applications. Express.js has list of middleware which makes developers easy to quickly set up servers, define routes, and handle HT
2 min read
How to integrate Express-rate-limit in Node.js ?
Rate limiting prevents the same IP from making too many requests that will help us prevent attacks like brute force. The express-rate-limit is the npm package for limiting the request from the user. Project Setup: Run the following sets of commands to create a folder and initialize the project. mkdi
2 min read
How to create a simple HTTP server in Node ?
NodeJS is a powerful runtime environment that allows developers to build scalable and high-performance applications, especially for I/O-bound operations. One of the most common uses of NodeJS is to create HTTP servers. What is HTTP?HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used for transferri
3 min read