A hollow cylinder is a 3D shape that’s empty inside with some thickness around the edges. The formula for its total surface area (TSA) is:
TSA of Hollow Cylinder = 2πh (R + r) + 2π(R² – r²)
Here are formulas for other areas of a hollow cylinder:
- Lateral Surface Area (LSA): 2πh (R + r)
- Cross-Sectional Area: π(R2 − r2)
where,
- R is Radius of Outer Circle
- r is Radius of Inner Circle
What is Hollow Cylinder?
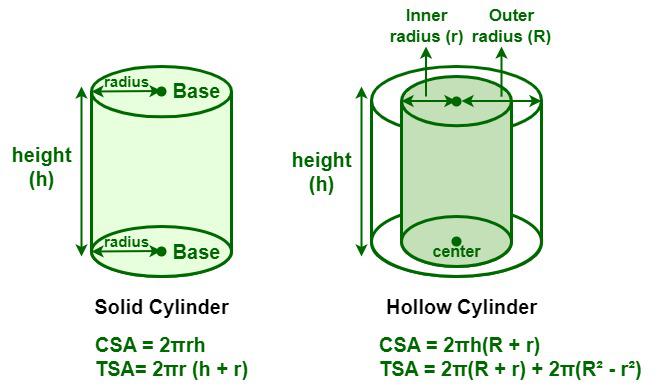
A hollow cylinder is a cylinder that is hollow from the inside. A hollow cylinder is defined as a three-dimensional object that is empty from the inside. In a hollow cylinder, there are two circular bases in the shape of rings. The circular base has two radii a smaller inner radius and a bigger outer radius.

Elements of a Hollow Cylinder
Hollow Cylinder Definition
A hollow cylinder is defined as a cylinder that is empty from the inside and has a difference between the internal and external radius.
There is some thickness enclosed between the inner radius and the outer radius, of the hollow cylinder, the thickness between them is equal to the difference between the internal and external radius. The height, of the hollow cylinder, is the perpendicular distance between its two circular bases.
Some examples of hollow cylinders are water pipes, straws, water bottles, etc.
Finding area of a hollow cylinder is similar to finding area of a cylinder. A hollow cylinder has two types of surface areas, i.e., a curved surface area and a total surface area.
- Curved surface area, or lateral surface area, is the surface area of the curved surface of the hollow cylinder.
- Total surface area of the hollow cylinder is the sum of its curved surface area and the areas of its two circular bases.
Curved Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder
Now, let’s calculate the curved surface area of the hollow cylinder. The curved surface area (CSA) of the hollow cylinder is equal to the sum of the external surface area (ESA) and the internal surface area (ISA) of the cylinder.
Let C1 be the outer circumference and C2 be the inner circumference of the given cylinder.
Thickness of the hollow cylinder (t) = R − r
We know that,
Circumference of a circle (C) = 2πr
So, C1 = 2πR and C2 = 2πr
CSA = ESA + ISA
We know that,
Curved Surface Area of a solid cylinder = C × h = 2πrh
CSA = 2πR × h + 2πr × h
CSA= 2πRh + 2πrh
CSA = 2πh (R + r)
Curved Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder = 2πh (R + r) square units
where,
- “h” is Height of Hollow Cylinder
- “R” is Outer Radius of Cylinder
- “r” is Inner Radius of Cylinder
Total Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder
Total surface area A of a hollow cylinder is the sum of the areas of its outer curved surface and its inner curved surface, along with the areas of the two circular bases.
Total Surface Area = Curved Surface Area + Areas of Bases
Let A1 be the area enclosed by the inner radius, r, and A2 be the area enclosed by the outer radius, R.
We know that the area of a circle (A) = πr2
So, A1 = πR2 and A2 = πr2
Now, the cross-sectional area of the base of the hollow cylinder (A) = A1 − A2
A = πR2 − πr2 = π((R² – r²)
TSA = CSA + 2 × A
= 2πh (R + r) + 2 × π(R² – r²)
TSA = 2πh (R + r) + 2π(R² – r²)
Total Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder = [2πh (R + r) + 2π(R² – r²)] square units
where,
- “h” is Height of Hollow Cylinder
- “R” is Outer Radius of Cylinder
- “r” is Inner Radius of Cylinder
Total Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder with One Side Open
A hollow cylinder with one side open is essentially a tube-like structure with an open end. This type of cylinder is commonly found in various industrial, architectural, and household applications, such as bottles and containers.
The total surface area of a hollow cylinder with one side open includes the outer curved surface area, the inner curved surface area, and the area of the closed end. To calculate the total surface area, we consider the following components:
- Outer Curved Surface Area (OCSA): This is the surface area of the outer curved surface of the cylinder. It is calculated using the formula 2πRh, where R is the outer radius of the cylinder and h is the height.
- Inner Curved Surface Area (ICSA): Similarly, the inner curved surface area of the cylinder is calculated using the same formula 2πrh, where r is the inner radius of the cylinder.
- Area of Closed End (ACE): Since one end of the cylinder is closed, we need to consider the surface area of the circular closed end. The area of the closed end is calculated using the formula 2πr2, where r is the inner radius.
Therefore, the total surface area (TSA) of the hollow cylinder with one side open is the sum of the outer curved surface area, the inner curved surface area, and the area of the closed end:
TSA = OCSA + ICSA + ACE
TSA = 2πRh + 2πrh + πr2
Total Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder with No Sides Open
When considering a hollow cylinder with no sides open, we are essentially referring to a solid cylinder with two closed ends. In this case, the total surface area includes the outer curved surface, the inner curved surface, and the areas of both the top and bottom ends.
To calculate the total surface area of a hollow cylinder with no sides open, we need to consider the following components:
- Outer Curved Surface Area (OCSA): The outer curved surface area of the cylinder is given by 2πRh, where R is the outer radius of the cylinder and h is the height.
- Inner Curved Surface Area (ICSA): The inner curved surface area of the cylinder is also 2πrh, where r is the inner radius.
- Area of Top and Bottom Ends: Since both ends of the cylinder are closed, we need to account for the areas of both the top and bottom circular ends. Each end has an area of 2πR2.
Therefore, the total surface area (TSA) of the hollow cylinder with no sides open is the sum of the outer curved surface area, the inner curved surface area, and the areas of both top and bottom ends:
TSA = OCSA + ICSA + Area of Top End + Area of Bottom End
TSA = 2πRh + 2πrh + πR2 + πR2
TSA = 2πRh + 2πrh + 2πR2
How to Find Area of Hollow Cylinder?
Let’s take an example to understand how to calculate the area of a hollow cylinder.
Example: Calculate the area of a hollow cylinder whose external radius is 12 cm, the internal radius is 9 cm, and the height is 7 cm.
Solution:
Step 1: Note the values of the given dimensions. Here, the external radius (R) is 12 cm, the internal radius (r) is 9 cm, and the height (h) is 7 cm.
Step 2: We know that the formula to find the area (TSA) of a hollow cylinder is [2πh (R + r) + 2π(R² – r²)] square units. Now, substitute the given values in the formula.
Step 3: Thus, the area of a hollow cylinder is calculated as
TSA = 1319.469 Square Meters
Questions on Area of Hollow Cylinder
Question 1: Calculate the area of a hollow cylinder whose external radius is 8 cm, the internal radius is 4 cm, and the height is 12 cm. [Use π= 22/7]
Solution:
- External Radius = 8 cm
- Internal Radius = 4 cm
- Height = 12 cm
We know that,
Area of Hollow Cylinder = 2πh (R + r) + 2π(R2 – r2)
= 2 × (22/7) × 12 × (8 + 4) + 2 × (22/7) × (82 – 42)
= 2 × (22/7) × 10 × 15 + 2 × (22/7) × 48
= 905.142 + 301.714
= 1,206.856 sq. cm.
Hence, area of a hollow cylinder is 1,206.856 sq. cm.
Question 2: Calculate the area of a hollow cylinder whose external radius is 6 m, the internal radius is 2 m, and the height is 8 m [Use π= 22/7]
Solution:
- External Radius = 6 m
- Internal Radius = 2 m
- Height = 8 m
We know that,
Area of the hollow cylinder = 2πh(R + r) + 2π(R2 – r2)
= 2 × (22/7) × 8 × (6 + 2) + 2 × (22/7) × (62 – 22)
= 2 × (22/7) × 8 × 8 + 2 × (22/7) × (36-4)
= 2 × (22/7) × 64 +2 × (22/7) × 32
= 352/7 × 64 + 64/7 × 32
=22528/7 + 2048/7
= 24576/7
= 3503.429 sq .m
Hence, area of a hollow cylinder is 603.429 sq. m.
Question 3: Ram has a hollow cylindrical pipe with him, and he was asked to find its curved surface area. The external radius of the pipe is 10 inches, the internal radius is 6 inches, and the height is 14 inches. [Use π= 22/7]
Solution:
- External Radius = 6 m
- Internal Radius = 2 m
- Height = 8 m
We know that,
Curved Surface Area of a Hollow cylinder = 2πh (R + r)
= 2 × (22/7) × 14 × (10 + 6)
= 2 × (22/7) × 14 × 16
= 1,408 sq. in
Hence, curved surface area of given hollow cylindrical pipe is 1,408 sq. in.
Question 4: Calculate the curved surface area of a hollow cylinder whose outer diameter is 26 cm, the inner diameter is 18 cm, and the height is 12 cm. [Use π= 22/7]
Solution:
Outer Diameter = 26 cm
- So, external Radius (R) = 26 cm/ 2 = 13 cm
Inner Diameter = 18 cm
- So, Internal Radius (r) = 18 cm/2 = 9 cm
Height = 12 cm
We know that,
Curved Surface Area of a Hollow cylinder = 2πh (R + r)
= 2 × (22/7) × 12 × (13 + 9)
= 2 × (22/7) × 12 × 22
= 1,659.428 sq. cm
Hence, curved surface area of given hollow cylindrical pipe is 1,659.428 sq. cm.
Examples of Hollow Cylinder
Following are a few examples of hollow cylinders:
- Pipes and Tubes: Pipes used in plumbing systems and tubes used in various industrial applications are examples of hollow cylinders. They have a cylindrical shape with a hollow interior, allowing fluids, gases, or other materials to pass through.
- Paper Towel Rolls: Paper towel rolls typically have a hollow cylindrical shape. The cardboard tube in the center provides structural support and allows the paper towels to be rolled onto and dispensed from the tube.
- Oil Barrels: Standard oil barrels used for storage and transportation of oil and other liquids have a hollow cylindrical shape. They are made of metal and have a sealed top and bottom to prevent leakage.
- Hollow Drums: Musical instruments like certain types of drums, such as the steelpan or hang drum, have a hollow cylindrical shape. The sound is produced by striking or vibrating the surface of the drum.
- Roller Bearings: Roller bearings used in machinery and automotive applications often have a hollow cylindrical shape. The inner and outer rings of the bearing form hollow cylinders, and the rolling elements fit between them.
FAQs on Hollow Cylinder
What is a hollow cylinder? Give some examples of a hollow cylinder.
A hollow cylinder can be defined as a three-dimensional geometric object that is empty from the inside. A hollow cylinder consists of two circular bases that have inner and outer radii. Straws, water pipes, tubes, toilet paper rolls, etc. are some examples of hollow cylinders that we see in our daily lives.
What is the formula to calculate the thickness of a hollow cylinder?
Thickness of a hollow cylinder is the enclosed space between the inner radius and the outer radius, which is equal to the difference between the internal and external radius.
Thickness of hollow cylinder (t) = R − r
What is formula to calculate curved surface area of a hollow cylinder?
Curved surface area, or lateral surface area, is the surface area of the curved surface of a hollow cylinder that is equal to the sum of the external surface area (ESA) and the internal surface area (ISA) of the cylinder.
Curved Surface Area of Hollow Cylinder = 2πh (R + r) square units
What is annular ring of a hollow cylinder?
Circular bases of a hollow cylinder are similar to an annular ring, which is a region bounded by two concentric circles. So, area of the circular base of the hollow cylinder is equal to the area of the annular ring of the cylinder.
What is formula to calculate volume of a hollow cylinder?
Formula to calculate the volume of a hollow cylinder is given as follows:
Volume of Hollow Cylinder = π(R2 – r2)h cubic units
What is area of hollow cylinder face?
Area of the two faces of a hollow cylinder is the difference between the outer and inner circular faces.
Area of Two Faces = 2π(r2outer − r2inner)
What is area of a half cylinder?
Area of a half cylinder includes curved surface area and the area of the circular base. It can be calculated using the formula (1/2)×2πr2 + πrh.
What is cylindrical area of cylinder?
Cylindrical area of a cylinder refers to the total surface area of the cylinder, including both the curved surface area and the area of the two circular bases. It can be calculated using the formula 2πr2+2πrh
What is the cross sectional area of a cylinder?
Coss-sectional area of a cylinder is the area of the circular shape formed by slicing the cylinder perpendicular to its axis. It is equal to the area of the base circle and can be calculated using the formula 2πr2
Similar Reads
Mensuration in Maths
Mensuration is a branch of mathematics that deals with measuring geometric figures, including their length, area, volume, and surface area. It provides formulas and techniques for calculating these attributes for 2D (plane) shapes and 3D (solid) objects. Types of Mensuration 2D Mensuration- Deals wi
3 min read
Introduction to Mensuration
Geometric Shapes in Maths
Geometric shapes are mathematical figures that represent the forms of objects in the real world. These shapes have defined boundaries, angles, and surfaces, and are fundamental to understanding geometry. Geometric shapes can be categorized into two main types based on their dimensions: 2D Shapes (Tw
2 min read
Visualizing Solid Shapes
Visualizing Solid Shapes: Any plane or any shape has two measurements length and width, which is why it is called a two-dimensional(2D) object. Circles, squares, triangles, rectangles, trapeziums, etc. are 2-D shapes. If an object has length, width, and breadth then it is a three-dimensional object(
8 min read
Volume of Combination of Solids
When two or more two solids are combined and the combination comes out useful, a shape that can be found in reality is called a combination of solids. When Solids are taught, the major focus is always on the point of their real-life use and applications, For example, a cylinder can be seen in Pipes
9 min read
Mensuration Formulas
Mensuration is the branch of geometry that deals with the measurement of area, length, or volume in 2D and 3D shapes. The 2D and 3D shapes are often called geometric shapes. In this article, we have curated all the mensuration formulas for various 2-D and 3-D shapes in detail. Types of Geometrical S
11 min read
Perimeter
Perimeter of Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its three sides. A triangle is a polygon with three sides, three vertices, and three angles. It is the simplest closed polygon in geometry, as it is the first possible closed figure. Any polygon can be divided into triangles. For instance, a quadril
5 min read
How to find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle?
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is equal to 3 x a, where a is the length of any sideAn Equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal and the angles are also equal. The value of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60 degrees therefore, it is also known as an equi
6 min read
Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
A triangle can be considered as an isosceles triangle if and only if two sides of the triangle have the same length and two equal angles. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle comes under the parent topic mensuration which is a branch of geometry that deals with measurements of 2D/3D figures. Perim
5 min read
Perimeter of Rectangle
A rectangle is a two-dimensional plane quadrilateral, with opposite sides equal and all four angles equal. The perimeter of a rectangle can be defined as the sum of the length of all four sides in a rectangle. Perimeter of rectangle is the total length of the boundary or the sum of all its sides. In
7 min read
Perimeter of Square | Formula, Derivation, Examples
A square is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with the following properties. All sides are of equal length, and each angle is a right angle (90°). It is a type of rectangle where the length and width are the same.A square also has the property that its diagonals are equal in length and bisect eac
4 min read
Perimeter of a Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a type of quadrilateral with four equal sides with opposite sides equal. Its sides do not intersect each other. There are two diagonals of a parallelogram that intersect each other at the center. A diagonal divides the parallelogram into two equal parts or triangles. The following
8 min read
Perimeter of A Rhombus
Perimeter of a Rhombus is the sum of all the sides of the rhombus. In a rhombus, all the sides are equal so the perimeter of the rhombus is 4 times its side. The perimeter of Rhombus is calculated by the formula P = 4a where a is the side length of the perimeter. Now we can also find the perimeter o
6 min read
How to Find the Perimeter of a Trapezium?
Suppose the sides of a Trapezium are a, b, c, and d then the Perimeter of the Trapezium is (a + b + c + d) units.Trapezium is a quadrilateral in which one pair of opposite sides are parallel. The perimeter of the trapezium is the sum of the boundaries of the trapezium. Suppose the sides of the trape
12 min read
Circumference of Circle - Definition, Perimeter Formula, and Examples
The circumference of a circle is the distance around its boundary, much like the perimeter of any other shape. It is a key concept in geometry, particularly when dealing with circles in real-world applications such as measuring the distance traveled by wheels or calculating the boundary of round obj
7 min read
Area
Area of a Triangle | Formula and Examples
The area of the triangle is a basic geometric concept that calculates the measure of the space enclosed by the three sides of the triangle. The formulas to find the area of a triangle include the base-height formula, Heron's formula, and trigonometric methods. The area of triangle is generally calcu
6 min read
Area of Equilateral Triangle
The area of an equilateral triangle is the amount of space enclosed within its three equal sides. For an equilateral triangle, where all three sides and all three internal angles are equal (each angle measuring 60 degrees), the area can be calculated using the formula [Tex]\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\times a
6 min read
Right Angled Triangle | Properties and Formula
Right Angle Triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees or right angle (90°). It is also known as the right triangle. In a right triangle, the two shorter sides called the perpendicular and the base, meet at the right angle (90°), while the longest side, opposite t
7 min read
Heron's Formula
Heron's formula is a popular method for calculating the area of a triangle when the lengths of its three sides are known. It was introduced by Heron of Alexandria in his book "Metrica". This formula applies to all types of triangles, including right-angled, equilateral, and isosceles. According to t
9 min read
Area of Square
The area of a Square is defined as the space enclosed by the boundary of the square. Measurement of the area is done in square units. The unit for measurement of the area is m2. Let's understand the Area of square with the following illustration: To calculate square's area we need to know the length
7 min read
Area of Rectangle
Area of the Rectangle is the region covered inside the boundaries of the rectangle. The area of a rectangle is calculated using its dimensions length and breadth similar to the square in which the side is both the length and breadth. To find the area, you multiply the length of the rectangle by its
10 min read
Area of Parallelogram | Definition, Formulas & Examples
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) where opposite sides are parallel and equal in length. In a parallelogram, the opposite angles are also equal, and the diagonals bisect each other (they cut each other into two equal parts). The area of a Parallelogram is the space or the regio
9 min read
Area of Rhombus: Formula, Derivation and Examples
Rhombus is a parallelogram in which all four sides are equal and opposite pairs of lines are congruent. The opposite angles in a rhombus are equal. It is a special type of parallelogram in which all sides are equal to each other. The internal angle of the Rhombus is not mandatory to be a right angle
8 min read
Area of Trapezoid Formula
Area of a trapezoid is a concept in geometry that helps to calculate the space enclosed by the unique quadrilateral. Basically it is measured in square units. In this article we will discuss in detail how to find the area of a trapezoid. Before going to the formula of the area of the trapezoid let's
9 min read
Area of a Circle: Formula, Derivation, Examples
The area of a Circle is the measure of the two-dimensional space enclosed within its boundaries. It is mostly calculated by the size of the circle's radius which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge. The area of a circle is proportional to the radius of the circle.
10 min read
How to Calculate Area of Sector of Circle?
Area of the sector is easily calculated by using various formulas of geometry. In this article, we have covered a definition of sector circles, types of sectors, and others in detail. Table of Content Sector DefinitionTypes of SectorsFormula for Area of a SectorExamples on Area of Sector of CircleFA
5 min read
Segment of a Circle
Segment of a Circle is one of the important parts of the circle other than the sector. As we know, the circle is a 2-D shape in which points are equidistant from the point and the line connecting the two points lying on the circumference of the circle is called the chord of the circle. The area form
7 min read
Find the area of the shaded region formed by the intersection of four semicircles in a square
Given the length of the side of a square a, the task is to find the area of the shaded region formed by the intersection of four semicircles in a square as shown in the image below: Examples: Input: a = 10 Output: 57Input: a = 19 Output: 205.77 Approach: Area of the shaded region will be: Area(semic
4 min read
3D Shape
Volume of a Cube
Volume of a Cube is defined as the total number of cubic units occupied by the cube completely. A cube is a three-dimensional solid figure, having 6 square faces. Volume is nothing but the total space occupied by an object. An object with a larger volume would occupy more space. The volume of the cu
9 min read
Diagonal of a Cube Formula
Diagonal of a cube is the line segment joining the two non-adjacent vertices of a Cube. The diagonal of a cube formula helps us to calculate the length of diagonals in a cube. There are primarily two diagonals in a cube, namely face diagonals and body diagonals. In this article, we will learn the ty
8 min read
Volume of Cuboid | Formula and Examples
Volume of a cuboid is calculated using the formula V = L × B × H, where V represents the volume in cubic units, L stands for length, B for breadth, and H for height. Here, the breadth and width of a cuboid are the same things. The volume signifies the amount of space occupied by the cuboid in three
8 min read
Volume of a Sphere
The volume of a sphere helps us understand how much space a perfectly round object occupies, from tiny balls to large planets. Using the simple volume of sphere formula, you can easily calculate the space inside any sphere. Whether you're curious about the volume of a solid sphere in math or science
8 min read
Volume of Hemisphere
Volume of a shape is defined as how much capacity a shape has or we can say how much material was required to form that shape. A hemisphere, derived from the Greek words "hemi" (meaning half) and "sphere," is simply half of a sphere. If you imagine slicing a perfectly round sphere into two equal hal
6 min read
Volume of Cone- Formula, Derivation and Examples
Volume of a cone can be defined as the space occupied by the cone. As we know, a cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape with a circular base and a single apex (vertex). Let's learn about Volume of Cone in detail, including its Formula, Examples, and the Frustum of Cone. Volume of ConeA cone's v
10 min read
Volume of a Cylinder| Formula, Definition and Examples
Volume of a cylinder is a fundamental concept in geometry and plays a crucial role in various real-life applications. It is a measure which signifies the amount of material the cylinder can carry. It is also defined as the space occupied by the Cylinder. The formula for the volume of a cylinder is π
11 min read
Mensuration 3D - Hollow sphere
In this article we shall calculate the volume, Curved surface area (CSA) and Total surface area of a hollow sphere or a spherical shell. Below shown is a diagram of a hollow sphere. As we can see in the figure, the outer radius of hollow sphere is ‘R’ and the inner radius is ‘r’. Volume of hollow sp
2 min read
Volume of a Hollow Cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional object that is formed when a rectangle is rotated along any of its sides. A hollow cylinder is one type of cylinder that is hollow from the inside. A hollow cylinder can be defined as a three-dimensional geometric object that is empty from the inside. A hollow cylin
8 min read
Convert Cubic Meter To Liter (m³ to l)
Cubic meter and Liter are the two most common metric units of volume. A mathematical quantity that is used to measure the amount of three-dimensional space that is occupied is called volume. It is usually measured numerically by using SI-derived units (like the cubic meter and liter) or various impe
6 min read
Total Surface Area
Surface Area of Cube | Curved & Total Surface Area
Surface area of a cube is defined as the total area covered by all the faces of a cube. In geometry, the cube is a fascinating three-dimensional object that we encounter daily, from dice to ice cubes. But have you ever wondered about the total area that covers a cube? This is what we call the surfac
15 min read
Surface Area of Cuboid
The surface area of a cuboid is the total space occupied by all its surfaces/sides. In geometry, a three-dimensional shape having six rectangular faces is called a cuboid. A cuboid is also known as a regular hexahedron and has six rectangular faces, eight vertices, and twelve edges with congruent, o
12 min read
Surface Area of Sphere | Formula, Derivation and Solved Examples
A sphere is a three-dimensional object with all points on its surface equidistant from its center, giving it a perfectly round shape. The surface area of a sphere is the total area that covers its outer surface. To calculate the surface area of a sphere with radius r, we use the formula: Surface Are
8 min read
Surface Area of a Hemisphere
A hemisphere is a 3D shape that is half of a sphere's volume and surface area. The surface area of a hemisphere comprises both the curved region and the base area combined. Hemisphere's Total Surface Area (TSA) = Curved Surface Area + Base Area = 3πr² square units.Curved Surface Area (CSA) = 2πr² sq
13 min read
Surface Area of Cone
Surface Area of a Cone is the total area encompassing the circular base and the curved surface of the cone. A cone has two types of surface areas. If the radius of the base is 'r' and the slant height is 'l', we use two formulas: Total Surface Area (TSA) of the cone = πr(r + l)Curved Surface Area (C
8 min read
Surface Area of Cylinder | Curved and Total Surface Area of Cylinder
Surface Area of a Cylinder is the amount of space covered by the flat surface of the cylinder's bases and the curved surface of the cylinder. The total surface area of the cylinder includes the area of the cylinder's two circular bases as well as the area of the curving surface. The volume of a cyli
10 min read
Lateral or Curved Surface Area