Designing Instagram | System Design
Last Updated :
17 Jan, 2024
Designing Instagram is an important topic for system design interview questions. Instagram follows strong Architecture. In this article, we will discuss the architecture of posting photos and videos, following and unfollowing users, liking and disliking posts, searching photos and videos, and generating news feeds.

Important Topics for Instagram System Design
1. What is Instagram?
Instagram is an American photo and video-sharing social networking service owned by Meta Platforms. It allows users to upload media that can be edited with filters, be organized by hashtags, and be associated with a location via geographical tagging. Posts can be shared publicly or with preapproved followers.
2. Requirements for Instagram System Design
2.1 Functional Requirements for Instagram System Design
In functional Requirements, we will not discuss the login or signup page of Instagram. Login and Signup architecture is the same for everyone. We will look for further like posting photos, etc.
- Post photos and videos: The users can post photos and videos on Instagram.
- Follow and unfollow users: The users can follow and unfollow other users on Instagram.
- Like or dislike posts: The users can like or dislike posts of the accounts they follow.
- Search photos and videos: The users can search photos and videos based on captions and location.
- Generate news feed: The users can view the news feed consisting of the photos and videos (in chronological order) from all the users they follow.
2.2 Non-Functional requirements for Instagram System Design
- Scalability: The system should be scalable to handle millions of users in terms of computational resources and storage.
- Latency: The latency to generate a news feed should be low.
- Availability: The system should be highly available.
- Durability: Any uploaded content (photos and videos) should never get lost.
- Consistency: We can compromise a little on consistency. It is acceptable if the content (photos or videos) takes time to show in followers’ feeds located in a distant region.
- Reliability: The system must be able to tolerate hardware and software failures.
3. Capacity Estimation for Instagram System Design
We have 1 billion users, with 500 million as daily active users. Assume 60 million photos and 35 million videos are shared on Instagram per day. We can consider 3 MB as the maximum size of each photo and 150 MB as the maximum size of each video uploaded on Instagram.On average, each user sends 20 requests (of any type) per day to our service.
3.1 Storage Per Day
Photos: 60 million photos/day * 3 MB = 180 TeraBytes / day
Videos: 35 million videos/day * 150 MB = 5250 TB / day
Total content size = 180 + 5250 = 5430 TB
The Total Space required for a Year:
5430 TB/day * 365 (days a year) = 1981950 TB = 1981.95 PetaBytes
3.2 Bandwidth Estimation
5430 TB/(24 * 60* 60) = 5430 TB/86400 sec ~= 62.84 GB/s ~= 502.8 Gbps
Incoming bandwidth ~= 502.8 Gbps
Let’s say the ratio of readers to writers is 100:1.
Required outgoing bandwidth ~= 100 * 502.8 Gbps ~= 50.28 Tbps
4. Use Case Diagram for Instagram System Design
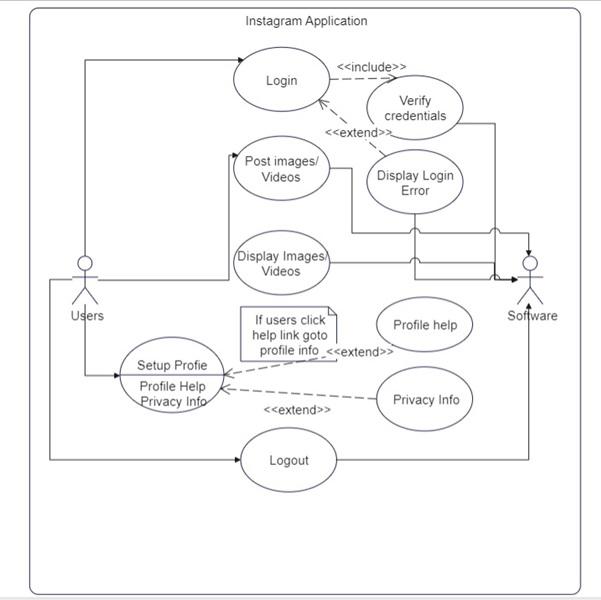 Use Case Diagram Instagram
Use Case Diagram InstagramIn the above Diagram we have discussed about the use case diagram of Instagram:
- If the user is new, they will register firstly it will be store in database, they will verifiy the profile.
- If user is already signup, they will provide the email-Id and Password.
- On the home page they will get the photos and videos, as well as the story page.
- The post which is posted now, it will come at the top. User can follow or unfollow the person. User can get live. It's all depend on them.
- There will be setting, in which user can see there past story or the post which has been archive. User can unblock the person they can get verified account, after paying.
5. Low-Level Design(LLD) for Instagram System Design
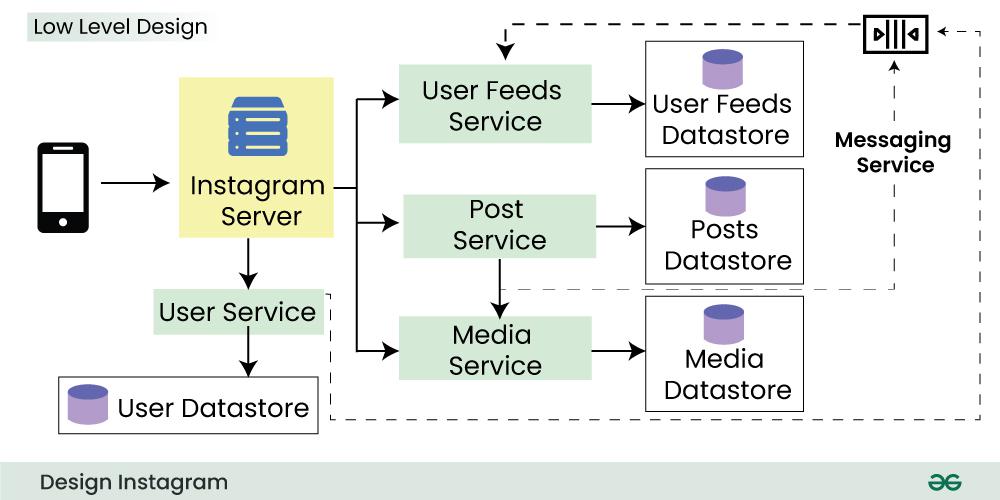
Here's a breakdown of the key components and interactions for Instagram's low-level design:
- User Service:
- Handles user registration, login, authentication, and profile management.
- Stores user data like username, email, bio, profile picture, etc.
- Integrates with social authentication providers (e.g., Facebook, Google).
- Post Service:
- Handles photo and video uploads, editing, and deletion.
- Stores post metadata like caption, hashtags, location, timestamp, etc.Processes uploaded media for resizing, filtering, and thumbnail generation.
- Manages photo and video transcoding for different devices and resolutions.
- Feed Service:
- Generates personalized news feeds for each user based on their follows, likes, activity, and engagement.
- Leverages a distributed system like Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ for real-time updates and notifications.
- Utilizes a cache layer like Redis for fast feed retrieval and reduced database load.
- Storage Service:
- Stores uploaded photos and videos efficiently and reliably.
- Utilizes a scalable object storage solution like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Azure Blob Storage.
- Implements redundancy and disaster recovery mechanisms for data protection.
- Search Service:
- Enables searching for users, hashtags, and locations.
- Indexes users, posts, and hashtags based on relevant parameters.
- Employs efficient indexing and search algorithms for fast and accurate results.
- Comment Service:
- Handles adding, editing, and deleting comments on posts.
- Tracks comment threads and parent-child relationships.
- Notifies users of new comments on their own posts or comments they participated in.
- Notification Service:
- Informs users about relevant events like likes, comments, mentions, and follows.
- Pushes notifications to mobile devices through platforms like Firebase Cloud Messaging or Amazon SNS.
- Leverages a queueing system for asynchronous notification delivery.
- Analytics Service:
- Tracks user engagement, post performance, and overall platform usage.
- Gathers data on views, likes, comments, shares, and clicks.
- Provides insights to improve user experience, optimize content recommendations, and target advertising.
Why we need caching for storing the data?
- Cache the data to handle millions of reads. It improves the user experience by making the fetching process fast. We’ll also opt for lazy loading, which minimizes the client’s waiting time.
- It allows us to load the content when the user scrolls and therefore save the bandwidth and focus on loading the content the user is currently viewing. It improves the latency to view or search a particular photo or video on Instagram.
6. High-Level Design(HLD) for Instagram System Design
Our system should allow us to upload, view, and search images and videos at a high level. To upload images and videos, we need to store them, and upon fetching, we need to retrieve the data from the storage. Moreover, the users should also be allowed to follow each other.
At a high level, Instagram can be viewed as a system with the following key components and interactions:
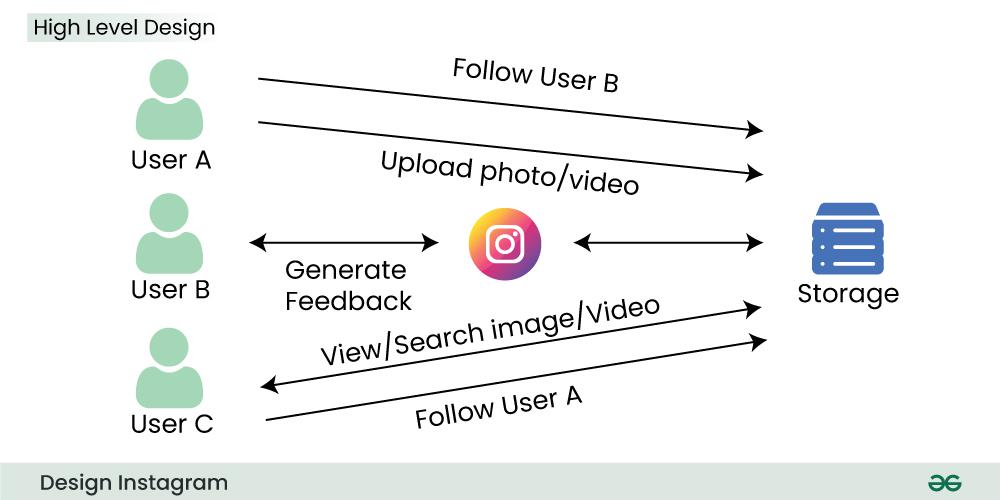
Components:
- Client: Mobile apps, web app, and APIs providing interface for users to interact with the system.
- Authentication & Authorization: Handles user login, registration, and access control.
- Content Management: Manages user-generated content like photos, videos, live streams, stories, and messages.
- Feed Generation: Personalizes news feeds for each user based on their follows, activity, and engagement.
- Social Graph: Tracks relationships between users (follows, followers, friends).
- Discovery & Search: Enables searching for users, hashtags, locations, and content.
- Notifications: Informs users about relevant events like likes, comments, mentions, and follows.
- Analytics & Reporting: Tracks user engagement, content performance, and overall platform usage.
Interactions:
- User creates content:
- Client uploads photo/video.
- Content Management stores media and metadata.
- Feed Generation updates user's and relevant followers' feeds.
- Notifications inform interested users.
- User interacts with content:
- Client sends like/comment/share actions.
- Content Management and Social Graph update relevant data.
- Feed Generation potentially reshuffles feeds based on new interactions.
- Notifications inform interested users.
- User discovers new content:
- Client uses search functionalities.
- Discovery & Search identifies relevant content.
- Client displays search results.
- User manages connections:
- Client sends follow/unfollow requests.
- Social Graph updates connections.
- Feed Generation adjusts based on changed relationships.
- User monitors activity:
- Client checks notifications feed.
- Notifications provide updates on relevant events.
Key Design Considerations:
- Scalability: System should handle millions of users and massive data volumes.
- Performance: Deliver fast response times for user interactions and content delivery.
- Reliability: Ensure high availability and prevent data loss.
- Security: Protect user data and privacy.
- Engagement: Design features that encourage user interaction and content creation.
7. API Design for Instagram System Design
7.1 Post photos and videos
Here's a potential API design for uploading photos and videos to Instagram:
Endpoints:
- POST /media: Submits a new photo or video.
- PUT /media/{media_id}: Updates existing metadata for a media item.
- DELETE /media/{media_id}: Deletes a media item.
Request
import requests
url = 'https://api.instagram.com/media' # Replace with the actual API endpoint URL
access_token = 'your_access_token' # Replace with the user's valid access token
# Define file path, caption, hashtags, and location (adjust as needed)
file_path = 'path/to/your/photo_or_video.jpg' # Or .mp4 for videos
caption = 'Your caption for the media'
hashtags = 'photography,nature,beautiful'
location = {"latitude": 37.421998, "longitude": -122.084269}
# Prepare headers and files for the request
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}',
'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data'
}
files = {
'file': open(file_path, 'rb'),
'caption': caption,
'hashtags': hashtags,
'location': str(location) # Location needs to be serialized as a string
}
# Send the POST request
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files)
# Handle the response
if response.status_code == 201:
data = response.json()
print('Media uploaded successfully!')
print('Media ID:', data['media_id'])
print('URL:', data['url'])
else:
print('Upload failed:', response.text)
print('Error details:', response.json()) # Display any error details
{
"media_id": "1234567890abcdef",
"url": "https://instagram.com/p/12345678",
"created_at": "2024-01-09T18:34:00Z",
"updated_at": "2024-01-09T18:34:00Z"
}