What is DFD(Data Flow Diagram)?
Last Updated :
04 Oct, 2024
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) represents the flow of data within information systems. Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) provide a graphical representation of the data flow of a system that can be understood by both technical and non-technical users. The models enable software engineers, customers, and users to work together effectively during the analysis and specification of requirements.
What is Data Flow Diagram (DFD)?
DFD is the abbreviation for Data Flow Diagram. The flow of data in a system or process is represented by a Data Flow Diagram (DFD). It also gives insight into the inputs and outputs of each entity and the process itself. Data Flow Diagram (DFD) does not have a control flow and no loops or decision rules are present. Specific operations, depending on the type of data, can be explained by a flowchart. It is a graphical tool, useful for communicating with users, managers and other personnel. it is useful for analyzing existing as well as proposed systems.
It should be pointed out that a DFD is not a flowchart. In drawing the DFD, the designer has to specify the major transforms in the path of the data flowing from the input to the output. DFDs can be hierarchically organized, which helps in progressively partitioning and analyzing large systems.
It provides an overview of
- What data is system processes.
- What transformation are performed.
- What data are stored.
- What results are produced , etc.
Data Flow Diagram can be represented in several ways. The Data Flow Diagram (DFD) belongs to structured-analysis modeling tools. Data Flow diagrams are very popular because they help us to visualize the major steps and data involved in software-system processes.
For a comprehensive introduction to DFDs and their applications, the System Design Course offers a clear and structured learning experience, ideal for system designers.
Characteristics of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Below are some characteristics of Data Flow Diagram (DFD):
- Graphical Representation: Data Flow Diagram (DFD) use different symbols and notation to represent data flow within system. That simplify the complex model.
- Problem Analysis: Data Flow Diagram (DFDs) are very useful in understanding a system and can be effectively used during analysis. Data Flow Diagram (DFDs) are quite general and are not limited to problem analysis for software requirements specification.
- Abstraction: Data Flow Diagram (DFD) provides a abstraction to complex model i.e. DFD hides unnecessary implementation details and show only the flow of data and processes within information system.
- Hierarchy: Data Flow Diagram (DFD) provides a hierarchy of a system. High- level diagram i.e. 0-level diagram provides an overview of entire system while lower-level diagram like 1-level DFD and beyond provides a detailed data flow of individual process.
- Data Flow: The primary objective of Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is to visualize the data flow between external entity, processes and data store. Data Flow is represented by an arrow Symbol.
- Ease of Understanding: Data Flow Diagram (DFD) can be easily understand by both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Modularity: Modularity can be achieved using Data Flow Diagram (DFD) as it breaks the complex system into smaller module or processes. This provides easily analysis and design of a system.
Types of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
There are two types of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- Logical Data Flow Diagram
- Physical Data Flow Diagram
Logical Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Logical data flow diagram mainly focuses on the system process. It illustrates how data flows in the system. Logical Data Flow Diagram (DFD) mainly focuses on high level processes and data flow without diving deep into technical implementation details. Logical DFD is used in various organizations for the smooth running of system. Like in a Banking software system, it is used to describe how data is moved from one entity to another.
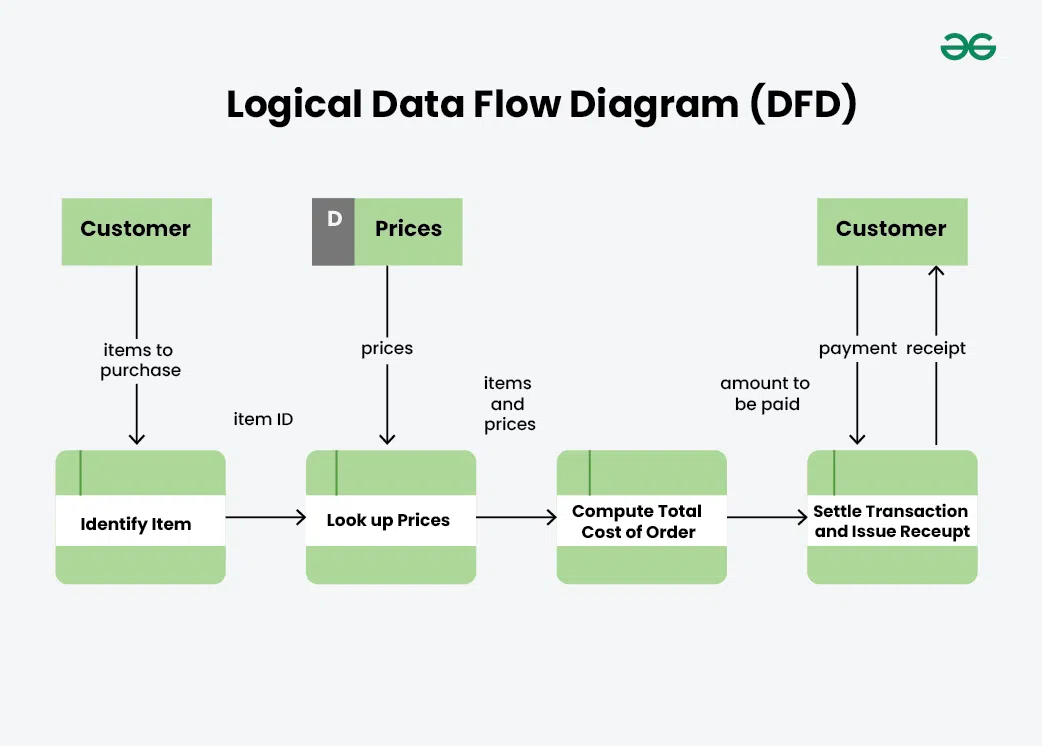
Logical Data Flow Diagram of Online Grocery Store
Physical data flow diagram shows how the data flow is actually implemented in the system. In the Physical Data Flow Diagram (DFD), we include additional details such as data storage, data transmission, and specific technology or system components. Physical DFD is more specific and close to implementation.

Physical Data Flow Diagram of online Grocery Store
Components of Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
The Data Flow Diagram has 4 components:
- Process: Input to output transformation in a system takes place because of process function. The symbols of a process are rectangular with rounded corners, oval, rectangle or a circle. The process is named a short sentence, in one word or a phrase to express its essence
- Data Flow: Data flow describes the information transferring between different parts of the systems. The arrow symbol is the symbol of data flow. A relatable name should be given to the flow to determine the information which is being moved. Data flow also represents material along with information that is being moved. Material shifts are modeled in systems that are not merely informative. A given flow should only transfer a single type of information. The direction of flow is represented by the arrow which can also be bi-directional.
- Warehouse (Data Store) : The data is stored in the warehouse for later use. Two horizontal lines represent the symbol of the store. The warehouse is simply not restricted to being a data file rather it can be anything like a folder with documents, an optical disc, a filing cabinet. The data warehouse can be viewed independent of its implementation. When the data flow from the warehouse it is considered as data reading and when data flows to the warehouse it is called data entry or data updating.
- Terminator (External Entity): The Terminator is an external entity that stands outside of the system and communicates with the system. It can be, for example, organizations like banks, groups of people like customers or different departments of the same organization, which is not a part of the model system and is an external entity. Modeled systems also communicate with terminator.

Basic Structure of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
What symbols and notations are used to represent Components of DFD?
In Data-Flow Diagrams (DFDs), symbols and notations vary depending on the methodology being used. Here’s a summary of symbols and notations commonly associated with each methodology:
The different methodologies or approaches used for creating Data-Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are:
- Gane and Sarson
- Yourdon and De Marco
- SSADM
- UML
Each methodology provides its own set of guidelines, symbols, and notations for representing system components and their interactions.
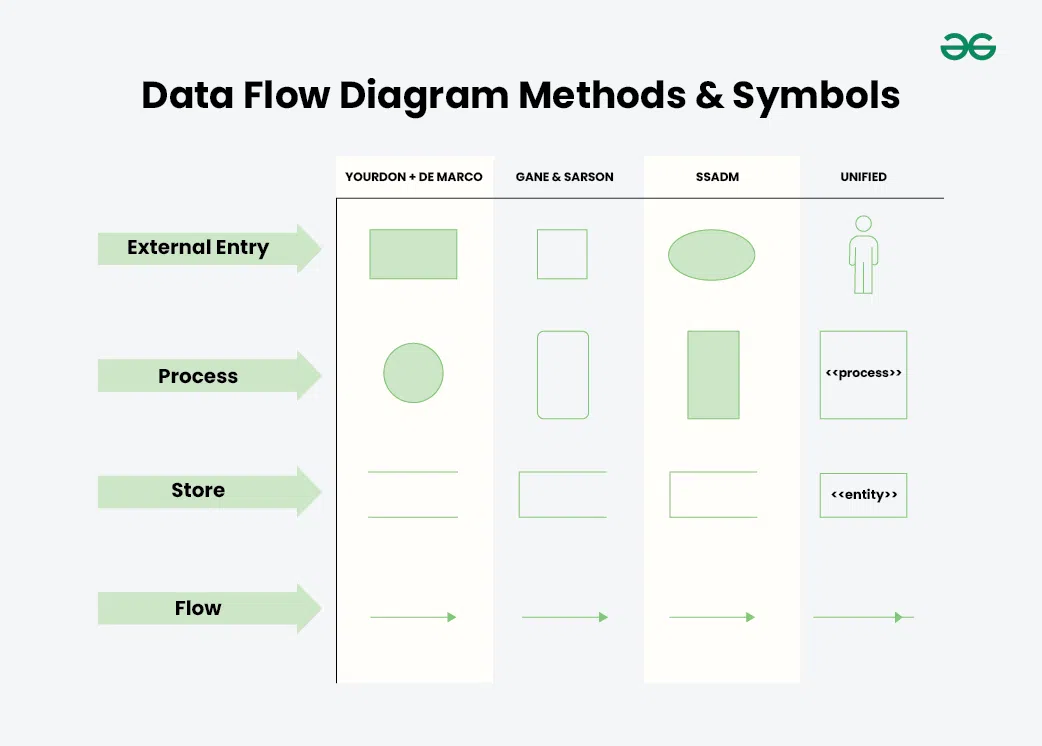
Data Flow Diagram Methods and Symbol
Levels of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) uses hierarchy to maintain transparency thus multilevel Data Flow Diagram (DFD’s) can be created. Levels of Data Flow Diagram (DFD) are as follows:
0-level DFD
It is also known as a context diagram. It’s designed to be an abstraction view, showing the system as a single process with its relationship to external entities. It represents the entire system as a single bubble with input and output data indicated by incoming/outgoing arrows.
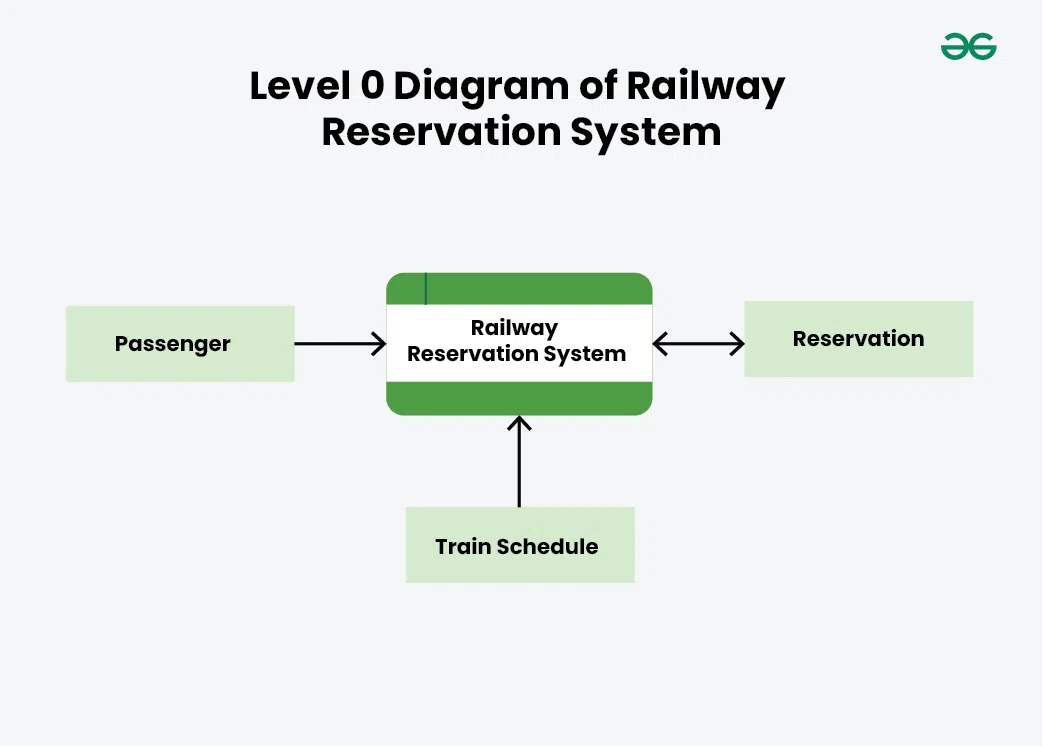
Level 0 of Railway Reservation System
This level provides a more detailed view of the system by breaking down the major processes identified in the level 0 DFD into sub-processes. Each sub-process is depicted as a separate process on the level 1 DFD. The data flows and data stores associated with each sub-process are also shown. In 1-level DFD, the context diagram is decomposed into multiple bubbles/processes. In this level, we highlight the main functions of the system and breakdown the high-level process of 0-level DFD into subprocesses.
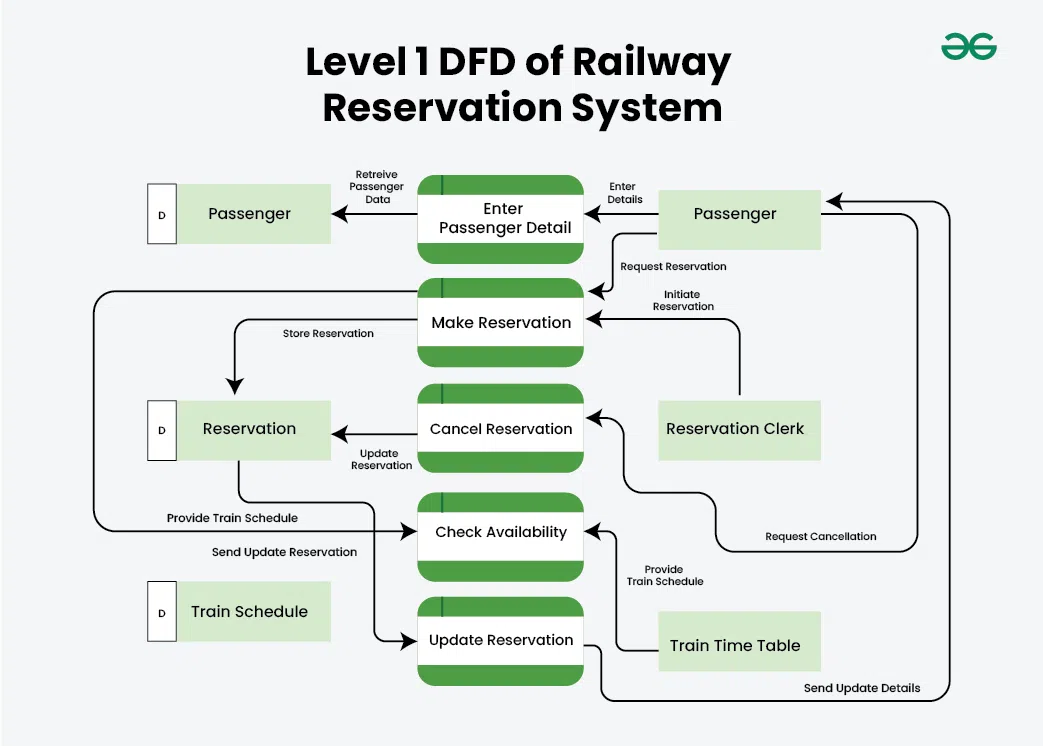
Level 1 DFD of Railway Reservation System
This level provides an even more detailed view of the system by breaking down the sub-processes identified in the level 1 DFD into further sub-processes. Each sub-process is depicted as a separate process on the level 2 DFD. The data flows and data stores associated with each sub-process are also shown.
Rules for Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Following are the rules of DFD:
- Data can flow from:
- Terminator or External Entity to Process
- Process to Terminator or External Entity
- Process to Data Store
- Data Store to Process
- Process to Process
- Data Cannot Flow From
- Terminator or External Entity to Terminator or External Entity
- Terminator or External Entity to Data Store
- Data Store to Terminator or External Entity
- Data Store to Data Store
Advantages of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- It helps us to understand the functioning and the limits of a system.
- It is a graphical representation which is very easy to understand as it helps visualize contents.
- Data Flow Diagram represent detailed and well explained diagram of system components.
- It is used as the part of system documentation file.
- Data Flow Diagrams can be understood by both technical or nontechnical person because they are very easy to understand.
Disadvantages of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- At times Data Flow Diagram (DFD) can confuse the programmers regarding the system.
- Data Flow Diagram takes long time to be generated, and many times due to this reasons analysts are denied permission to work on it.
How to Draw Data Flow Diagram?
Following are the steps to Draw Data Flow Diagram
- Understand the System
- Identify External Entities
- Identify Processes
- Identify Data Stores
- Use Standard Symbols
- Create Level 0 Diagram
- Based on Complexity Draw Further Level Diagram like Level 1, 2 and so on.
- Identify Data Flows:
- Number Processes and Data Stores
- Review and Validate
Conclusion
Data Flow Diagram ( DFD) are visual maps that provides a clear understanding of how information moves within a information system. Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) consist of four component i.e. Processes that represent system’s functionality, External Entities that represent the end users, data store that represent database or data ware house and data flow that represent how data are flow among these three components. DFD help everyone, from computer experts to regular users, as it provide a clear understanding of how a system works and how different parts of it interact. By using DFDs, people can work together effectively to analyze, design, and communicate about systems.
What are the 4 components of DFD?
Four Components of DFD are:
- Process
- Data Flow
- Data Store
- External Entity
What are the symbols used in DFD?
Symbols Used in DFD are standardized notations, like rectangles, circles, arrows, and short-text labels.
What are the levels of DFD?
Levels in DFD are numbered 0, 1, 2 or beyond.
Is flowchart a DFD?
No, Both are different. A flowchart illustrates the sequence of steps or actions within a process, detailing the logic and decision points, while a Data-Flow Diagram (DFD) focuses on representing the flow of data within a system, showing how data moves between processes, data stores, and external entities without specifying the sequence of actions.